每每忘记细节引起争辩,得有个地方把所有相关知识点收集起来
1.1. 接口
按如下代码顺序讲解接口:
#define MAX_EVENTS 10
struct epoll_event ev, events[MAX_EVENTS];
int listen_sock, conn_sock, nfds, epollfd;
/* Code to set up listening socket, 'listen_sock',
(socket(), bind(), listen()) omitted */
epollfd = epoll_create1(0);
if (epollfd == -1) {
perror("epoll_create1");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
ev.data.fd = listen_sock;
if (epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, listen_sock, &ev) == -1) {
perror("epoll_ctl: listen_sock");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for (;;) {
nfds = epoll_wait(epollfd, events, MAX_EVENTS, -1);
if (nfds == -1) {
perror("epoll_wait");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for (n = 0; n < nfds; ++n) {
if (events[n].data.fd == listen_sock) {
conn_sock = accept(listen_sock,
(struct sockaddr *) &addr, &addrlen);
if (conn_sock == -1) {
perror("accept");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
setnonblocking(conn_sock);
ev.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
ev.data.fd = conn_sock;
if (epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, conn_sock,
&ev) == -1) {
perror("epoll_ctl: conn_sock");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
} else {
do_use_fd(events[n].data.fd);
}
}
}
1.1.1. epoll_event
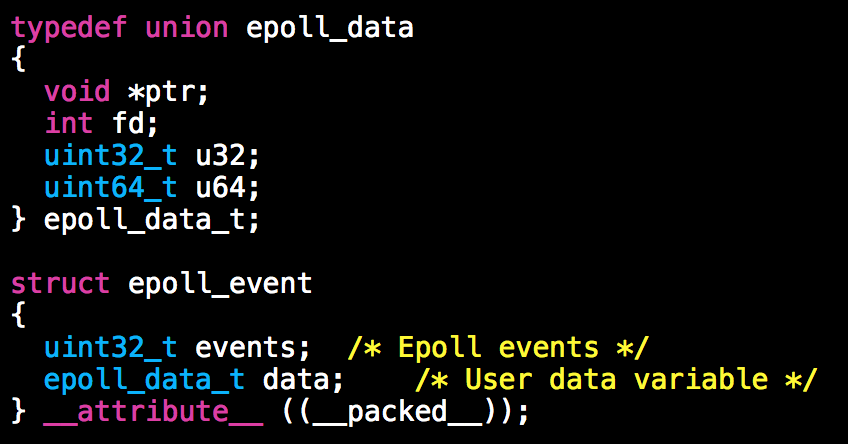
struct epoll_event ev; ev.events = EPOLLIN; ev.data.fd = listen_sock; 要被监听事件的fd,在上例中是个listenfd
1.1.2. epoll_create
/* Creates an epoll instance. Returns an fd for the new instance.
The "size" parameter is a hint specifying the number of file
descriptors to be associated with the new instance. The fd
returned by epoll_create() should be closed with close(). */
extern int epoll_create (int __size) __THROW;
创建一个epoll队列,返回该epoll队列的fd。 这个入参__size在linux内核2.6.8+就不再用了,保留参数是为了向下兼容。
记得对fd调用close
size相关解释:In the initial epoll_create() implementation, the size argument informed the kernel of the number of file descriptors that the caller expected to add to the epoll instance. The kernel used this information as a hint for the amount of space to initially allocate in internal data structures describing events. (If necessary, the kernel would allocate more space if the caller’s usage exceeded the hint given in size.) Nowadays, this hint is no longer required (the kernel dynamically sizes the required data structures without needing the hint), but size must still be greater than zero, in order to ensure backward compatibility when new epoll applications are run on older kernels.
1.1.3. epoll_create1
extern int epoll_create1 (int __flags) __THROW;
flag=0的话与epoll_create相同
可以传2个flag:
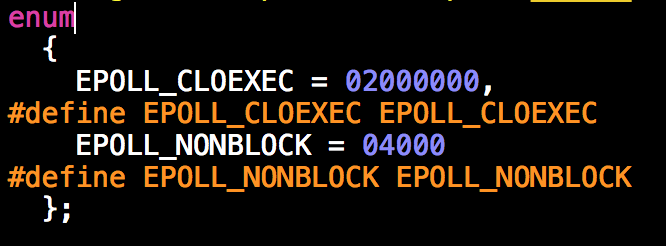
| EPOLL_CLOEXEC:(since Linux 2.6.23) 能够保证该epoll fd正确设置成“退出时关闭”(不用调用close),即使有fork也不会引起竞争导致fd泄露(比如 main create fd – fork – fcntl ( fd, F_SETFL, flag | O_CLOEXEC ) ) |
By default, the new file descriptor is set to remain open across an execve(2) .Note that the use of this flag is essential in some multithreaded programs, because using a separate fcntl(2)F_SETFD operation to set the FD_CLOEXEC flag does not suffice to avoid race conditions where one thread opens a file descriptor and attempts to set its close-on-exec flag using fcntl(2) at the same time as another thread does a fork(2) plus execve(2). Depending on the order of execution, the race may lead to the file descriptor returned by open() being unintentionally leaked to the program executed by the child process created by fork(2). (This kind of race is in principle possible for any system call that creates a file descriptor whose close-on-exec flag should be set, and various other Linux system calls provide an equivalent of the O_CLOEXEC flag to deal with this problem.)
EPOLL_NONBLOCK:epoll.h说是可以设置,但其实并没有文档解释。不好猜,暂时搁置
1.1.4. epoll_event.events
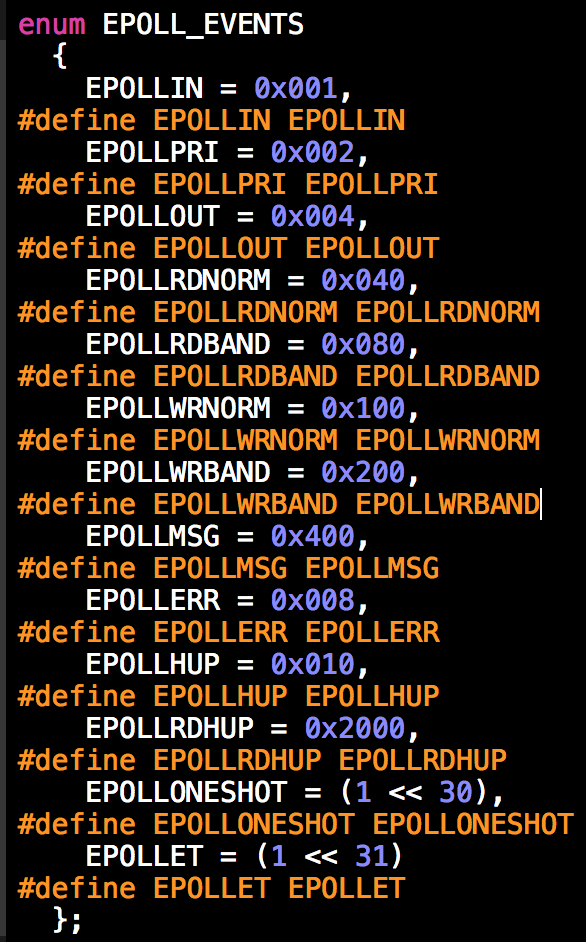
事件有:
EPOLLIN The associated file is available for read(2) operations. EPOLLOUT The associated file is available for write(2) operations. EPOLLRDHUP (since Linux 2.6.17) Stream socket peer closed connection, or shut down writing half of connection. (This flag is especially useful for writ‐ ing simple code to detect peer shutdown when using Edge Trig‐ gered monitoring.) EPOLLPRI There is an exceptional condition on the file descriptor. See the discussion of POLLPRI in poll(2). There is some exceptional condition on the file descriptor.
Possibilities include: * There is out-of-band data on a TCP socket (see tcp(7)). * A pseudoterminal master in packet mode has seen a state change on the slave (see ioctl_tty(2)). * A cgroup.events file has been modified (see cgroups(7)).
EPOLLERR 即使不设置也会被触发的 Error condition happened on the associated file descriptor. This event is also reported for the write end of a pipe when the read end has been closed. epoll_wait(2) will always report for this event; it is not necessary to set it in events. EPOLLHUP 即使不设置也会被触发的
Hang up happened on the associated file descriptor. epoll_wait(2) will always wait for this event; it is not nec‐ essary to set it in events. Note that when reading from a channel such as a pipe or a stream socket, this event merely indicates that the peer closed its end of the channel. Subsequent reads from the channel will return 0 (end of file) only after all outstanding data in the channel has been consumed. EPOLLET 事件设置为边沿触发 Sets the Edge Triggered behavior for the associated file descriptor. The default behavior for epoll is Level Trig‐ gered. See epoll(7) for more detailed information about Edge and Level Triggered event distribution architectures. EPOLLONESHOT (since Linux 2.6.2) fd只被触发一次 Sets the one-shot behavior for the associated file descriptor. This means that after an event is pulled out with epoll_wait(2) the associated file descriptor is internally disabled and no other events will be reported by the epoll interface. The user must call epoll_ctl() with EPOLL_CTL_MOD to rearm the file descriptor with a new event mask. EPOLLWAKEUP (since Linux 3.5) If EPOLLONESHOT and EPOLLET are clear and the process has the CAP_BLOCK_SUSPEND capability, ensure that the system does not enter “suspend” or “hibernate” while this event is pending or being processed. The event is considered as being “processed” from the time when it is returned by a call to epoll_wait(2) until the next call to epoll_wait(2) on the same epoll(7) file descriptor, the closure of that file descriptor, the removal of the event file descriptor with EPOLL_CTL_DEL, or the clear‐ ing of EPOLLWAKEUP for the event file descriptor with EPOLL_CTL_MOD. See also BUGS.
If the system is in autosleep mode via /sys/power/autosleep and an
event happens which wakes the device from sleep, the device driver will keep the device awake only until that event is queued. To keep the device awake until the event has been processed, it is necessary to use the epoll_ctl(2)EPOLLWAKEUP flag. When the EPOLLWAKEUP flag is set in the events field for a structepoll_event, the system will be kept awake from the moment the event is queued, through the epoll_wait(2) call which returns the event until the subsequent epoll_wait(2) call. If the event should keep the system awake beyond that time, then a separate wake_lock should be taken before the second epoll_wait(2) call.
EPOLLEXCLUSIVE (since Linux 4.5)
一个fd能被塞到多个epoll队列中,当fd有事件发生,会触发多个epoll_wait。本参数可用来解决惊群
比如一个fd被塞到了7个epoll队列中,其中3个event没有指定EPOLLEXCLUSIVE,4个event指定了EPOLLEXCLUSIVE。则当事件发生时,3个未指定参数的event都会被触发,4个指定参数的event中,至少有一个at least one会被触发
Sets an exclusive wakeup mode for the epoll file descriptor that is being attached to the target file descriptor, fd. When a wakeup event occurs and multiple epoll file descriptors are attached to the same target file using EPOLLEXCLUSIVE, one or more of the epoll file descriptors will receive an event with epoll_wait(2). The default in this scenario (when EPOLLEXCLUSIVE is not set) is for all epoll file descriptors to receive an event. EPOLLEXCLUSIVE is thus useful for avoid‐ ing thundering herd problems in certain scenarios. If the same file descriptor is in multiple epoll instances, some with the EPOLLEXCLUSIVE flag, and others without, then events will be provided to all epoll instances that did not specify EPOLLEXCLUSIVE, and at least one of the epoll instances that did specify EPOLLEXCLUSIVE. The following values may be specified in conjunction with EPOLLEXCLUSIVE: EPOLLIN, EPOLLOUT, EPOLLWAKEUP, and EPOLLET. EPOLLHUP and EPOLLERR can also be specified, but this is not required: as usual, these events are always reported if they occur, regardless of whether they are specified in events. Attempts to specify other values in events yield an error. EPOLLEXCLUSIVE may be used only in an EPOLL_CTL_ADD operation; attempts to employ it with EPOLL_CTL_MOD yield an error. If EPOLLEXCLUSIVE has been set using epoll_ctl(), then a subse‐ quent EPOLL_CTL_MOD on the same epfd, fd pair yields an error. A call to epoll_ctl() that specifies EPOLLEXCLUSIVE in events and specifies the target file descriptor fd as an epoll instance will likewise fail. The error in all of these cases is EINVAL.
1.1.5. epoll_ctl
/* Manipulate an epoll instance "epfd". Returns 0 in case of success,
-1 in case of error ( the "errno" variable will contain the
specific error code ) The "op" parameter is one of the EPOLL_CTL_*
constants defined above. The "fd" parameter is the target of the
operation. The "event" parameter describes which events the caller
is interested in and any associated user data. */
extern int epoll_ctl (int __epfd, int __op, int __fd,
struct epoll_event *__event) __THROW;
op合法参数有三个:
EPOLL_CTL_ADD:注册一个event
EPOLL_CTL_MOD:修改fd关联的的__event
EPOLL_CTL_DEL:把fd从epoll队列中删除,此时不关心__event内容,__event可以为NULL
1.1.5.1. 报错
EBADF epfd or fd is not a valid file descriptor. EEXIST op was EPOLL_CTL_ADD, and the supplied file descriptor fd is already registered with this epoll instance. EINVAL epfd is not an epoll file descriptor, or fd is the same as epfd, or the requested operation op is not supported by this interface. EINVAL An invalid event type was specified along with EPOLLEXCLUSIVE in events. EINVAL op was EPOLL_CTL_MOD and events included EPOLLEXCLUSIVE. EINVAL op was EPOLL_CTL_MOD and the EPOLLEXCLUSIVE flag has previously been applied to this epfd, fd pair. EINVAL EPOLLEXCLUSIVE was specified in event and fd refers to an epoll instance. ELOOP fd refers to an epoll instance and this EPOLL_CTL_ADD operation would result in a circular loop of epoll instances monitoring one another. ENOENT op was EPOLL_CTL_MOD or EPOLL_CTL_DEL, and fd is not registered with this epoll instance. ENOMEM There was insufficient memory to handle the requested op control operation. ENOSPC The limit imposed by /proc/sys/fs/epoll/max_user_watches was encountered while trying to register (EPOLL_CTL_ADD) a new file descriptor on an epoll instance. See epoll(7) for further details. EPERM The target file fd does not support epoll. This error can occur if fd refers to, for example, a regular file or a directory.
1.1.6. epoll_wait
/* Wait for events on an epoll instance "epfd". Returns the number of
triggered events returned in "events" buffer. Or -1 in case of
error with the "errno" variable set to the specific error code. The
"events" parameter is a buffer that will contain triggered
events. The "maxevents" is the maximum number of events to be
returned ( usually size of "events" ). The "timeout" parameter
specifies the maximum wait time in milliseconds (-1 == infinite).
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern int epoll_wait (int __epfd, struct epoll_event *__events,
int __maxevents, int __timeout);
/* Same as epoll_wait, but the thread's signal mask is temporarily
and atomically replaced with the one provided as parameter.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern int epoll_pwait (int __epfd, struct epoll_event *__events,
int __maxevents, int __timeout,
__const __sigset_t *__ss);
epoll_wait》
被触发的event会被放入入参__events中 (struct epoll_event events[MAX_EVENTS]),__maxevents 通常设置为events数组长度
__timeout 毫秒,-1表示阻塞
被触发的event数据结构中,epoll_data为调用epoll_ctl时传入的内容(所以是为了context传递用?)
epoll_pwait》
The following epoll_pwait() call: ready = epoll_pwait(epfd, &events, maxevents, timeout, &sigmask); is equivalent to atomically executing the following calls: sigset_t origmask; pthread_sigmask(SIG_SETMASK, &sigmask, &origmask); ready = epoll_wait(epfd, &events, maxevents, timeout); pthread_sigmask(SIG_SETMASK, &origmask, NULL);
1.1.6.1. ERRORS
EBADF epfd is not a valid file descriptor. EFAULT The memory area pointed to by events is not accessible with write permissions. EINTR The call was interrupted by a signal handler before either (1) any of the requested events occurred or (2) the timeout expired; see signal(7). EINVAL epfd is not an epoll file descriptor, or maxevents is less than or equal to zero.
1.2. Level-triggered and edge-triggered
水平触发和边沿触发,假设场景如下:
- pipe的read端对应句柄rfd,rfd在epoll中注册了读事件
- pipe被写入2kb数据
- epoll_wait被唤醒,代表rfd有可读事件了
- 从rfd读取1kb数据
- rfd重新塞回epoll set
如果rfd事件设置了EPOLLET,那么在第5步,即使在接收缓冲区中仍有1kb数据可读,但epoll_wait也不会被唤醒。
ET模式下,只有在”改变发生”的时刻 事件才会被触发 (edge-triggered mode delivers events only when changes occur on the monitored file descriptor)
ET使用建议:with nonblocking file descriptors;by waiting for an event only after read(2) or write(2) return EAGAIN.
1.3. Q&A
问:一个fd,能在一个epoll队列中被重复注册么?
答:一般会得到一个error EEXIST的,但如果这个fd已经设置了F_DUPFD,那么能注册两次。有用的地方是读、写事件可以分别注册分别触发
问:一个fd的相同事件,能注册到两个epoll队列中么?怎么触发?
答:能,都会被触发的
问:epoll队列自己的epoll_fd能塞到自己里么?
答:不能,会返回EINVAL,但能塞到其他epoll set里
问:创建epoll队列、然后fork,在父进程塞进去的event会唤醒两个进程么?
答:不知道,待试试。猜测不会
问:关闭一个fd,会将其自动从所有epoll set中移除么?
答:会。但这个场景要注意:fd1和fd2指向相同file description,fd1放到了epoll set中,如果只关闭了fd1没有关闭fd2,那么fd1是不会被自动移除了,并且fd1时间也可能被触发
Will closing a file descriptor cause it to be removed from all epoll sets automatically? Yes, but be aware of the following point. A file descriptor is a reference to an open file description (see open(2)). Whenever a file descriptor is duplicated via dup(2), dup2(2), fcntl(2)F_DUPFD, or fork(2), a new file descriptor referring to the same open file description is created. An open file description con‐ tinues to exist until all file descriptors referring to it have been closed. A file descriptor is removed from an epoll set only after all the file descriptors referring to the underlying open file description have been closed (or before if the file descriptor is explicitly removed using epoll_ctl(2)EPOLL_CTL_DEL). This means that even after a file descriptor that is part of an epoll set has been closed, events may be reported for that file descriptor if other file descriptors referring to the same under‐ lying file description remain open
问:到底能注册多少fds到epoll set里?
答:
这个文件约束一个用户总共能注册多少fd到epoll中(用户级别的limit,不是进程级别的)
一个注册fd的内存开销大约是 32核机器90bytes、64核机器160bytes,默认值是可用内存的4%
1.4. 参考资料-灰常有用
http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/epoll.7.html
http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/epoll_create.2.html
http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/epoll_ctl.2.html
http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/epoll_wait.2.html
